from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from src.langchain_docs_loader import load_langchain_docs_splitted
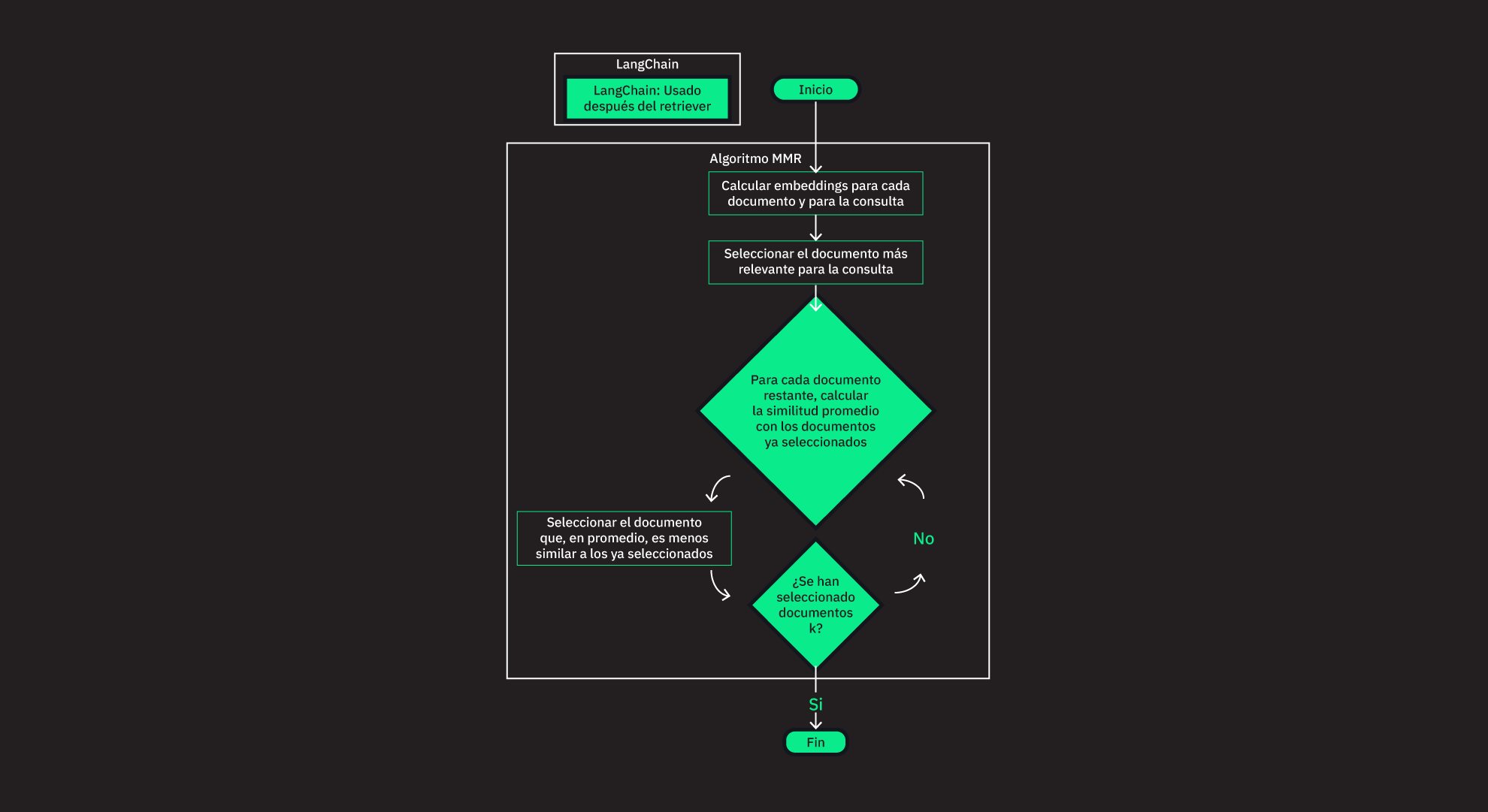
load_dotenv()TrueMMR es un método de re-ranking que combina la relevancia y la diversidad de los documentos recuperados. El objetivo es maximizar la relevancia de los documentos devueltos y minimizar la redundancia entre ellos.
Esto puede ser útil para incrementar la habilidad de los modelos de lenguage para generar respuestas con mayor cobertura y profundidad.
Su algoritmo es el siguiente:
embeddings para cada documento y para la consulta.k documentos. Es decir, una lista ordenada que parte del documento que más contribuye a la diversidad general hasta el documento que contribuye menos.En Langchain, el algoritmo de MMR es utilizado después de que el retriever ha recuperado los documentos más relevantes para la consulta. Por lo tanto, nos aseguramos que estamos seleccionando documentos diversos de un conjunto de documentos que ya son relevantes para la consulta.
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from src.langchain_docs_loader import load_langchain_docs_splitted
load_dotenv()Truedocs = load_langchain_docs_splitted()Normalmente creamos nuestro retriever de la siguiente manera:
similarity_retriever = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
).as_retriever(k=4)Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 792024 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 699650 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 606969 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..Sin embargo, podrás notar que de hacerlo, el tipo de búsqueda que se realiza es por similitud de vectores. En este caso, queremos realizar una búsqueda por similitud de vectores, pero con un re-ranking por relevancia marginal máxima (MMR).
similarity_retriever.search_type'similarity'Entonces, para crear un retriever con re-ranking por MMR, debemos hacer lo siguiente:
mmr_retriever = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
).as_retriever(
search_type="mmr",
k=4, # number of documents to retrieve after mmr
fetch_k=20, # number of documents to fetch in the first step
# Lambda mult is a number between 0 and 1 that determines the degree
# of diversity among the results with 0 corresponding to maximum diversity
# and 1 to minimum diversity.
lambda_mult=0.5,
)Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 768011 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 666659 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 558623 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 858146 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 759714 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 656845 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 8.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 554661 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 823705 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 731885 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..
Retrying langchain.embeddings.openai.embed_with_retry.<locals>._embed_with_retry in 4.0 seconds as it raised RateLimitError: Rate limit reached for default-text-embedding-ada-002 in organization org-vwqjdaXGZeEg6mWAVSflJXD9 on tokens per min. Limit: 1000000 / min. Current: 633547 / min. Contact us through our help center at help.openai.com if you continue to have issues..Ahora nuestro retriever está listo para ser utilizado con re-ranking por MMR.
mmr_retriever.search_type'mmr'similarity_retriever.get_relevant_documents(
"How to integrate LCEL into my Retrieval augmented generation system with a keyword search retriever?"
)[Document(page_content="# Retrieval\n\nMany LLM applications require user-specific data that is not part of the model's training set.\nThe primary way of accomplishing this is through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).\nIn this process, external data is _retrieved_ and then passed to the LLM when doing the _generation_ step.\n\nLangChain provides all the building blocks for RAG applications - from simple to complex.\nThis section of the documentation covers everything related to the _retrieval_ step - e.g. the fetching of the data.\nAlthough this sounds simple, it can be subtly complex.\nThis encompasses several key modules.\n\n\n\n**Document loaders**\n\nLoad documents from many different sources.\nLangChain provides over 100 different document loaders as well as integrations with other major providers in the space,\nlike AirByte and Unstructured.\nWe provide integrations to load all types of documents (HTML, PDF, code) from all types of locations (private s3 buckets, public websites).\n\n**Document transformers**\n\nA key part of retrieval is fetching only the relevant parts of documents.\nThis involves several transformation steps in order to best prepare the documents for retrieval.\nOne of the primary ones here is splitting (or chunking) a large document into smaller chunks.\nLangChain provides several different algorithms for doing this, as well as logic optimized for specific document types (code, markdown, etc).\n\n**Text embedding models**\n\nAnother key part of retrieval has become creating embeddings for documents.\nEmbeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, allowing you to quickly and\nefficiently find other pieces of text that are similar.\nLangChain provides integrations with over 25 different embedding providers and methods,\nfrom open-source to proprietary API,\nallowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs.\nLangChain provides a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between models.\n\n**Vector stores**\n\nWith the rise of embeddings, there has emerged a need for databases to support efficient storage and searching of these embeddings.\nLangChain provides integrations with over 50 different vectorstores, from open-source local ones to cloud-hosted proprietary ones,\nallowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs.\nLangChain exposes a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between vector stores.\n\n**Retrievers**\n\nOnce the data is in the database, you still need to retrieve it.\nLangChain supports many different retrieval algorithms and is one of the places where we add the most value.\nWe support basic methods that are easy to get started - namely simple semantic search.\nHowever, we have also added a collection of algorithms on top of this to increase performance.\nThese include:\n\n- [Parent Document Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/parent_document_retriever): This allows you to create multiple embeddings per parent document, allowing you to look up smaller chunks but return larger context.\n- [Self Query Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/self_query): User questions often contain a reference to something that isn't just semantic but rather expresses some logic that can best be represented as a metadata filter. Self-query allows you to parse out the _semantic_ part of a query from other _metadata filters_ present in the query.\n- [Ensemble Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/ensemble): Sometimes you may want to retrieve documents from multiple different sources, or using multiple different algorithms. The ensemble retriever allows you to easily do this.\n- And more!", metadata={'description': "Many LLM applications require user-specific data that is not part of the model's training set.", 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/', 'title': 'Retrieval | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content='PubMedPubMed® by The National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine comprises more than 35 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/pubmed)[📄️ RePhraseQueryRetrieverSimple retriever that applies an LLM between the user input and the query pass the to retriever.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/re_phrase)[📄️ SEC filings dataSEC filings data powered by Kay.ai and Cybersyn.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/sec_filings)[📄️ SVMSupport vector machines (SVMs) are a set of supervised learning methods used for classification, regression and outliers detection.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/svm)[📄️ TF-IDFTF-IDF means term-frequency times inverse document-frequency.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/tf_idf)[📄️ VespaVespa is a fully featured search engine and vector database. It supports vector search (ANN), lexical search, and search in structured data, all in the same query.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/vespa)[📄️ Weaviate Hybrid SearchWeaviate is an open source vector database.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/weaviate-hybrid)[📄️ WikipediaWikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system called MediaWiki. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read reference work in history.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/wikipedia)[📄️ ZepRetriever Example for Zep - A long-term memory store for LLM applications.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/zep_memorystore)', metadata={'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/retrievers', 'title': 'Retrievers | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content='### Going deeper\u200b\n\n- Agents, such as the [conversational retrieval agent](/docs/use_cases/question_answering/how_to/conversational_retrieval_agents), can be used for retrieval when necessary while also holding a conversation.', metadata={'description': 'Open In Collab', 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/chatbots', 'title': 'Chatbots | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content='## LLMRails as a Retriever\u200b\n\nLLMRails, as all the other LangChain vectorstores, is most often used as a LangChain Retriever:\n\n```python\nretriever = llm_rails.as_retriever()\nretriever\n```\n\n```text\n LLMRailsRetriever(tags=None, metadata=None, vectorstore=<langchain.vectorstores.llm_rails.LLMRails object at 0x107b9c040>, search_type=\'similarity\', search_kwargs={\'k\': 5})\n```\n\n```python\nquery = "What is your approach to national defense"\nretriever.get_relevant_documents(query)[0]\n```\n\n```text\n Document(page_content=\'But we will do so as the last resort and only when the objectives and mission are clear and achievable, consistent with our values and laws, alongside non-military tools, and the mission is undertaken with the informed consent of the American people.\\n\\nOur approach to national defense is described in detail in the 2022 National Defense Strategy.\\n\\nOur starting premise is that a powerful U.S. military helps advance and safeguard vital U.S. national interests by backstopping diplomacy, confronting aggression, deterring conflict, projecting strength, and protecting the American people and their economic interests.\\n\\nAmid intensifying competition, the military’s role is to maintain and gain warfighting advantages while limiting those of our competitors.\\n\\nThe military will act urgently to sustain and strengthen deterrence, with the PRC as its pacing challenge.\\n\\nWe will make disciplined choices regarding our national defense and focus our attention on the military’s primary responsibilities: to defend the homeland, and deter attacks and aggression against the United States, our allies and partners, while being prepared to fight and win the Nation’s wars should diplomacy and deterrence fail.\\n\\nTo do so, we will combine our strengths to achieve maximum effect in deterring acts of aggression—an approach we refer to as integrated deterrence (see text box on page 22).\\n\\nWe will operate our military using a campaigning mindset—sequencing logically linked military activities to advance strategy-aligned priorities.\\n\\nAnd, we will build a resilient force and defense ecosystem to ensure we can perform these functions for decades to come.\\n\\nWe ended America’s longest war in Afghanistan, and with it an era of major military operations to remake other societies, even as we have maintained the capacity to address terrorist threats to the American people as they emerge.\\n\\n20 NATIONAL SECURITY STRATEGY Page 21 \\x90\\x90\\x90\\x90\\x90\\x90\\n\\nA combat-credible military is the foundation of deterrence and America’s ability to prevail in conflict.\', metadata={\'type\': \'file\', \'url\': \'https://cdn.llmrails.com/dst_d94b490c-4638-4247-ad5e-9aa0e7ef53c1/c2d63a2ea3cd406cb522f8312bc1535d\', \'name\': \'Biden-Harris-Administrations-National-Security-Strategy-10.2022.pdf\'})\n```', metadata={'description': 'LLMRails is a API platform for building GenAI applications. It provides an easy-to-use API for document indexing and querying that is managed by LLMRails and is optimized for performance and accuracy.', 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/vectorstores/llm_rails', 'title': 'LLMRails | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'})]mmr_retriever.get_relevant_documents(
"How to integrate LCEL into my Retrieval augmented generation system with a keyword search retriever?"
)[Document(page_content="# Retrieval\n\nMany LLM applications require user-specific data that is not part of the model's training set.\nThe primary way of accomplishing this is through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).\nIn this process, external data is _retrieved_ and then passed to the LLM when doing the _generation_ step.\n\nLangChain provides all the building blocks for RAG applications - from simple to complex.\nThis section of the documentation covers everything related to the _retrieval_ step - e.g. the fetching of the data.\nAlthough this sounds simple, it can be subtly complex.\nThis encompasses several key modules.\n\n\n\n**Document loaders**\n\nLoad documents from many different sources.\nLangChain provides over 100 different document loaders as well as integrations with other major providers in the space,\nlike AirByte and Unstructured.\nWe provide integrations to load all types of documents (HTML, PDF, code) from all types of locations (private s3 buckets, public websites).\n\n**Document transformers**\n\nA key part of retrieval is fetching only the relevant parts of documents.\nThis involves several transformation steps in order to best prepare the documents for retrieval.\nOne of the primary ones here is splitting (or chunking) a large document into smaller chunks.\nLangChain provides several different algorithms for doing this, as well as logic optimized for specific document types (code, markdown, etc).\n\n**Text embedding models**\n\nAnother key part of retrieval has become creating embeddings for documents.\nEmbeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, allowing you to quickly and\nefficiently find other pieces of text that are similar.\nLangChain provides integrations with over 25 different embedding providers and methods,\nfrom open-source to proprietary API,\nallowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs.\nLangChain provides a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between models.\n\n**Vector stores**\n\nWith the rise of embeddings, there has emerged a need for databases to support efficient storage and searching of these embeddings.\nLangChain provides integrations with over 50 different vectorstores, from open-source local ones to cloud-hosted proprietary ones,\nallowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs.\nLangChain exposes a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between vector stores.\n\n**Retrievers**\n\nOnce the data is in the database, you still need to retrieve it.\nLangChain supports many different retrieval algorithms and is one of the places where we add the most value.\nWe support basic methods that are easy to get started - namely simple semantic search.\nHowever, we have also added a collection of algorithms on top of this to increase performance.\nThese include:\n\n- [Parent Document Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/parent_document_retriever): This allows you to create multiple embeddings per parent document, allowing you to look up smaller chunks but return larger context.\n- [Self Query Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/self_query): User questions often contain a reference to something that isn't just semantic but rather expresses some logic that can best be represented as a metadata filter. Self-query allows you to parse out the _semantic_ part of a query from other _metadata filters_ present in the query.\n- [Ensemble Retriever](/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/ensemble): Sometimes you may want to retrieve documents from multiple different sources, or using multiple different algorithms. The ensemble retriever allows you to easily do this.\n- And more!", metadata={'description': "Many LLM applications require user-specific data that is not part of the model's training set.", 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/', 'title': 'Retrieval | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content='### Going deeper\u200b\n\n- Agents, such as the [conversational retrieval agent](/docs/use_cases/question_answering/how_to/conversational_retrieval_agents), can be used for retrieval when necessary while also holding a conversation.', metadata={'description': 'Open In Collab', 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/chatbots', 'title': 'Chatbots | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content="[📄️ Amazon KendraAmazon Kendra is an intelligent search service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It utilizes advanced natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to enable powerful search capabilities across various data sources within an organization. Kendra is designed to help users find the information they need quickly and accurately, improving productivity and decision-making.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/amazon_kendra_retriever)[📄️ ArxivarXiv is an open-access archive for 2 million scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/arxiv)[📄️ Azure Cognitive SearchAzure Cognitive Search (formerly known as Azure Search) is a cloud search service that gives developers infrastructure, APIs, and tools for building a rich search experience over private, heterogeneous content in web, mobile, and enterprise applications.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/azure_cognitive_search)[📄️ BM25BM25 also known as the Okapi BM25, is a ranking function used in information retrieval systems to estimate the relevance of documents to a given search query.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/bm25)[📄️ ChaindeskChaindesk platform brings data from anywhere (Datsources: Text, PDF, Word, PowerPpoint, Excel, Notion, Airtable, Google Sheets, etc..) into Datastores (container of multiple Datasources).](/docs/integrations/retrievers/chaindesk)[📄️ ChatGPT PluginOpenAI plugins connect ChatGPT to third-party applications. These plugins enable ChatGPT to interact with APIs defined by developers, enhancing ChatGPT's capabilities and allowing it to perform a wide range of actions.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/chatgpt-plugin)[📄️ Cohere RerankerCohere is a Canadian startup that provides natural language processing models that help companies improve human-machine interactions.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/cohere-reranker)[📄️ DocArray RetrieverDocArray is a versatile, open-source tool for managing your multi-modal data. It lets you shape your data however you want, and offers the flexibility to store and search it using various document index backends. Plus, it gets even better - you can utilize your DocArray document index to create a DocArrayRetriever, and build awesome Langchain apps!](/docs/integrations/retrievers/docarray_retriever)[📄️ ElasticSearch BM25Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/elastic_search_bm25)[📄️ Google Cloud Enterprise SearchEnterprise Search is a part of the Generative AI App Builder suite of tools offered by Google Cloud.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/google_cloud_enterprise_search)[📄️ Google Drive RetrieverThis notebook covers how to retrieve documents from Google Drive.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/google_drive)[📄️ Kay.aiData API built for RAG 🕵️ We are curating the world's largest datasets as high-quality embeddings so your AI agents can retrieve context on the fly. Latest models, fast retrieval, and zero infra.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/kay)[📄️ kNNIn statistics, the k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. It is used for classification and regression.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/knn)[📄️ LOTR (Merger Retriever)Lord of the Retrievers, also known as MergerRetriever, takes a list of retrievers as input and merges the results of their getrelevantdocuments() methods into a single list. The merged results will be a list of documents that are relevant to the query and that have been ranked by the different retrievers.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/merger_retriever)[📄️ MetalMetal is a managed service for ML Embeddings.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/metal)[📄️ Pinecone Hybrid SearchPinecone is a vector database with broad functionality.](/docs/integrations/retrievers/pinecone_hybrid_search)[📄️ PubMedPubMed® by The National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine comprises more than 35 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science", metadata={'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/retrievers', 'title': 'Retrievers | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'}),
Document(page_content='### Use the Zep Retriever to vector search over the Zep memory\u200b\n\nZep provides native vector search over historical conversation memory. Embedding happens automatically.\n\nNOTE: Embedding of messages occurs asynchronously, so the first query may not return results. Subsequent queries will return results as the embeddings are generated.\n\n```python\nfrom langchain.retrievers import ZepRetriever\n\nzep_retriever = ZepRetriever(\n session_id=session_id, # Ensure that you provide the session_id when instantiating the Retriever\n url=ZEP_API_URL,\n top_k=5,\n api_key=zep_api_key,\n)\n\nawait zep_retriever.aget_relevant_documents("Who wrote Parable of the Sower?")', metadata={'description': 'Retriever Example for Zep - A long-term memory store for LLM applications.', 'language': 'en', 'source': 'https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/retrievers/zep_memorystore', 'title': 'Zep | 🦜️🔗 Langchain'})]